Introduction to Idgham
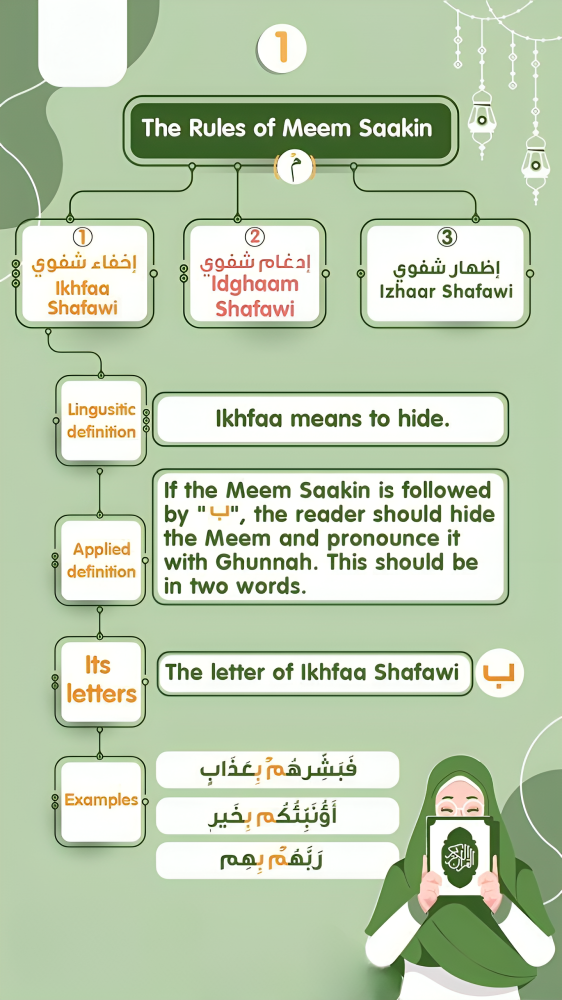
Idgham is a crucial concept in Tajweed, the set of rules governing the proper pronunciation of Quranic recitation. The term Idgham literally means “merging” or “blending,” and it refers to the process of merging one letter into another, causing changes in pronunciation that enhance the beauty and precision of Quranic recitation.
What is Idgham?
In Tajweed, Idgham occurs when a non-voweled consonant is followed by another consonant, resulting in the merging of these letters during recitation. This linguistic phenomenon is essential for maintaining the melodious and precise nature of Quranic recitation.
Types of Idgham
Scholars of Tajweed have identified two primary types of Idgham:
1. Idgham with Ghunnah
Idgham with Ghunnah involves merging certain letters while producing a nasal sound (ghunnah). This type occurs when specific letters merge, creating a distinctive nasal resonance.
Letters of Idgham with Ghunnah:
- Noon Sakinah and Tanwin merge with the following letters:
- ي (Ya)
- ن (Noon)
- م (Meem)
- و (Waw)
Examples:
- In the verse: مِّن يَوْمٍ (Min yawmin)
- The noon sakinah merges with the ya, producing a ghunnah sound
2. Idgham without Ghunnah
Idgham without Ghunnah differs from the first type as it does not produce the nasal resonance. This occurs when specific letters merge without the characteristic ghunnah sound.
Letters of Idgham without Ghunnah:
- Noon Sakinah and Tanwin merge with:
- ر (Ra)
- ل (Lam)
Examples:
- In the verse: مِن رَّبِّهِمْ (Min rabbihim)
- The noon sakinah merges with the ra without producing a ghunnah sound
Detailed Rules of Idgham
Idgham with Ghunnah Rules
- Complete Merging: The first letter (Noon Sakinah or Tanwin) completely disappears, and the second letter is pronounced with a ghunnah.
- Nasal Resonance: A slight nasal sound (ghunnah) is produced, lasting approximately two counts.
- Smooth Transition: The letters merge seamlessly, maintaining the rhythm of recitation.
Idgham without Ghunnah Rules
- Complete Merging: The first letter (Noon Sakinah or Tanwin) disappears entirely.
- No Nasal Sound: The merging occurs without any additional nasal resonance.
- Clear Pronunciation: The merged letter is pronounced clearly and distinctly.
Practical Application
How to Practice Idgham
- Listen to proficient Quranic reciters
- Practice with a qualified Tajweed instructor
- Use Tajweed learning resources and audio guides
- Focus on the subtle differences between Idgham types
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incomplete merging of letters
- Incorrect duration of ghunnah
- Failing to distinguish between Idgham with and without ghunnah
- Overlooking the precise pronunciation rules
Importance in Quranic Recitation
Mastering Idgham is not just about technical pronunciation but about:
- Preserving the linguistic beauty of the Quran
- Maintaining the precise oral tradition
- Showing respect for the divine text
- Enhancing the spiritual experience of recitation
Conclusion
Idgham represents a sophisticated aspect of Tajweed that requires dedicated practice and careful attention. By understanding and implementing these rules, reciters can approach the Quranic text with the reverence and precision it deserves.
Recommended Resources
- Tajweed textbooks
- Online Tajweed courses from Baytul Quran
- Local Quranic recitation classes
Note: Always seek guidance from qualified Tajweed instructors for comprehensive learning.